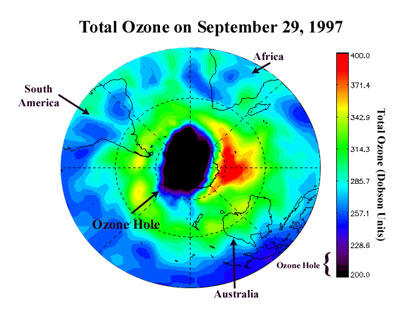
Ozone layer is a layer in the outer atmosphere (stratosphere) that contains the gas ozone, which acts as a shield in the atmosphere absorbing much of the harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the Sun, preventing them from reaching Earth's surface. It is a protective layer made up of oxygen, with a molecular formula of O3, lying 15 to 35 kilometres above Earth's surface, protecting life on Earth from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet rays. In the past century, the ozone layer is getting thinner and thinner. In 1987, a hole as big as United States developed over continent of Antarctica comes to be known as "Antarctic Ozone Hole". In 2000, the hole was at its largest, 3 times the size of United States.Urgent measures are needed to combat increasing ozone depletion as more harmful ultraviolet rays from the Sun can now reach the Earth.
Who is responsible for all these disastrous effects on Earth?
No doubt, it is humans. They have created CFC. CFCs developed in 1930s are man-made substances that contain chlorine, which are used as solvents in paints, propellants in aerosol sprays, coolants in refrigerators and air-conditioners, manufacturing of foam packaging and cleaning of electronic parts. They are compounds of carbon, chlorine and fluorine, with two main examples having molecular formulas of CFCl3 and CF2Cl2.
CFCs are harmless to the environment at ground level. However, once released, they rise up in the atmosphere and carried to the stratosphere. Under intense sunlight, they are broken down by UV rays from the Sun. CFCs decompose and release chlorine atoms which interact with ozone and convert it to oxygen. Chlorine atoms can destroy ozone molecules. One chlorine atom can destroy about 100000 ozone molecules, leading to ozone depletion. CFCs are very stable gases and remain for a very long time, from 100 to 20 000 years in the atmosphere, also, being difficult to destroy. Hence, though ozone layer can replace itself as ozone is continually created in the atmosphere as a result of the reaction of the Sun’s rays with oxygen in the atmosphere, CFCs, are being released at a faster rate than the rate at which ozone replaces itself.
How would ozone depletion affect the earth?
Ozone layer depletion reduces the protective ability environment from harmful ultraviolet rays of the Sun, which means greater exposure to harmful ultraviolet rays from the Sun. UV rays react with exhaust fumes, dust and smoke to produce smog (thick layer of pollutants) which worsens air quality in cities and weakens structures exposed to UV radiation. Too much ultraviolet radiation kills plankton, which is the basic food for marine life, leading to decline in fish supply. Aquatic/ marine creatures will die as the food chain is broken. Some aquatic species may be endangered. Increased exposure to UV rays also destroys or harms plant life because chlorophyll level reduces and plant tissues get damaged.This leads to poor harvest, decline in food supply and eventually starvation, e.g. rice. As plant growth is adversely affected, forest resources may decline and wildlife cum natural habitats become threatened.
There are also straightforward effects on human health. Increased exposure to harmful UV rays can cause skin cancer (melanoma) and eye cataracts (blurred vision) in people, which if left untreated, it can lead to blindness. Also, it weakens people's immune system, thus reducing resistance to illnesses and diseases.

No comments:
Post a Comment